Variables and Expressions
After completing this lesson, you will be able to:
- Evaluate expressions using the order of operations
In mathematics, we use the order of operations to perform
mathematical operations. Always follow this order when performing
operations:
- Simplify within grouping symbols first. Grouping symbols
include braces, \{ \} , brackets,[ ] ,and parentheses ( )
- Evaluate all exponents
- Perform all multiplication and division, left to right
- Perform all addition and subtraction, left to right
A good way to remember this is by the saying
Please Excuse My
Dear Aunt Salley
The first letter of each word stands for:
P - Parentheses
E - Exponents
M - Multiplication
D - Division
A - Addition
S - Subtraction
Example 1
Evaluate 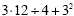
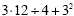 = = |
|
|
| |
3 · 12 ÷ 4 + 9 |
Since we have an exponent we do that
first 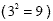 |
| |
36 ÷ 4 + 9 |
Since we have multiplication we do that
next ( 3 · 12 = 36 ) |
| |
9 + 9 |
Since we have division we do that next (
36 ÷ 4 = 9 ) |
| |
18 |
Last, we do the addition to achieve the
final answer of 18 |
Example 2
Evaluate 8 + 12 ÷ 3
| 8 + 12 ÷ 3 = |
|
|
| |
8 + 4 |
(Divide 12 by 3) |
| |
12 |
(Add 8 and 4) |
Example 3
Evaluate 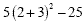
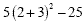 = = |
|
|
| |
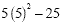 |
Complete the addition within the
parentheses first (2 + 3) |
| |
5(25) - 25 |
Evaluate the exponent 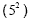 |
| |
125 - 25 |
Complete the multiplication ( 5 · 25 ) |
| |
100 |
Complete the subtraction |
Example 4
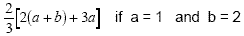
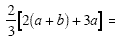 |
|
|
| |
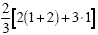 |
Since we are given values for a and b, we
substitute first |
| |
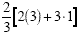 |
Complete the addition inside the
parentheses |
| |
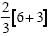 |
Complete the multiplication 2 times 3 and 3 times 1 |
| |
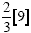 |
Add 6 and 3 |
| |
|
Multiply 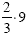 (This easily done by multiplying 2 times 9and
then dividing by 3) (This easily done by multiplying 2 times 9and
then dividing by 3) |
Example 5
Evaluate 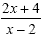 for x = 6 for x = 6
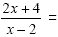 |
|
|
| |
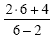 |
Substitute 6 for each x in the expression |
| |
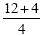 |
2 times 6 in the numerator and 6 minus 2
in the denominator |
| |
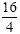 |
12 plus 4 |
| |
4 |
16 divided by 4 |
| 
